Table of Contents
Enabling the FS (File System) Provider
Introduction
The Nasuni Access Anywhere appliance allows a local folder, or file system, to be added as provider. This is particularly useful for network file servers and applications that can be mounted as file systems in Linux.
To connect using the CIFS protocol directly see Enabling the SMB/CIFS Connector.
(This guide assumes you are familiar with mounting file systems on linux)
By default the ability to add a file system storage provider is disabled within the appliance and for user packages. To enable follow these instructions:
Enable the FS provider for the Appliance
- Login as appladmin in to the appliance
- Go to Settings → Site Functionality
- Toward the bottom of the page under Providers ensure that FS Provider is enabled
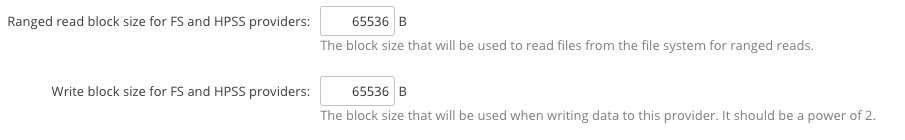
Tuning Block Size
In the same section you can also tune the block size used to read and write from the file system. The default value is 65536 (64KiB)
Enable the FS connector for the User Package
- Login as appladmin in to the appliance
- Go to Menu button in the top right of the screen → User Packages
- Select the package assigned to the user/organization
- Enable the FS provider for the package and save
Disable SELinux
Before you proceed further you will need to disable SELinux. Please follow the instructions Disable SELinux.
Mount the File System on Linux
Mount the file system on the appliance. If you need to create a new Linux user do so and note the password as you will need it in the next step.
Add FS to the account
Login in to the NAA user account and you should see FS as provider in the dropdown list when you login as NAA user
Enter the Linux user name and password. This is the linux user that has read/write access to the mounted file system.
Effective User
File system operations are performed by Access Anywhere as the Linux user who mounted the file system. Access permissions thus will be determined by both the Nasuni Access Anywhere and the network file system.
The ability to mount the file system for each Access Anywhere user may also be supported. Contact Access Anywhere support@nasuni.com for more information.
Using the FS Provider with NFS
The FS provider can be used to access NFS file systems through Access Anywhere. First the NFS file system must be mounted on Access Anywhere host by Access Anywhere's Linux system administrator. Once it has been mounted, it can be added to Access Anywhere using the FS connector.
When mounting an NFS file system on the Linux host you may want to use a mount point like:
/mnt/NFS/<NFS_sharename>/
That way you can have two or more NFS file systems in the same location in the directory tree.