**This is an old revision of the document!**
Understanding file timestamps
Access Anywhere stores file metadata including filenames and timestamps. It does not store file data.
Some timestamp metadata is synchronized with that of the storage provider. This may be different for different types of storage. Other timestamp metadata is created by Access Anywhere based on file activity.
1 File modified times
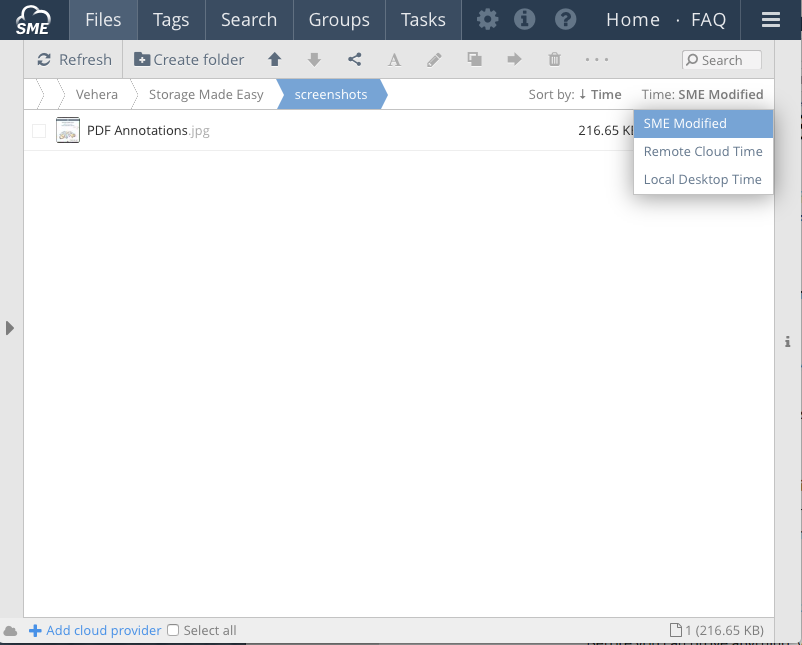
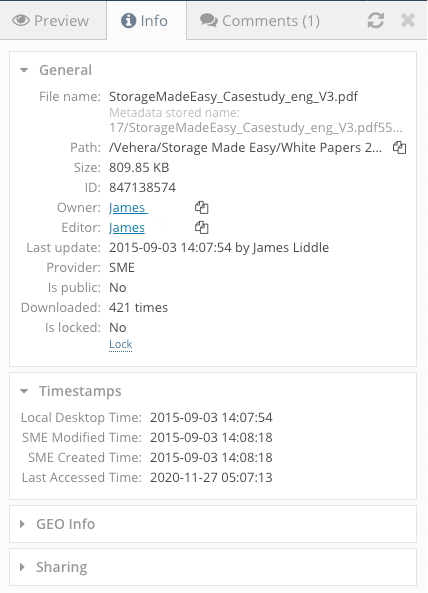
Hovering over the time field or looking at the file info pane in the Web Browser shows 4 different times:
- Storage Created Time - This is the time the file was indexed by Access Anywhere in UTC format
- Storage Modified Time - The last modified time for the file in UTC format
- Local Desktop Time- The local modified time for the file, converted to UTC format (for the browser this will be based on the browser locale settings)
- Remote Cloud Time - The modified timestamp that was received from a files metadata, converted to UTC, from a mapped storage provider.
2 Uploading files from the web
If files are uploaded from the web File Manager then original modified timestamps are preserved except for the Safari browser which will use the timestamp of when the files was uploaded for the modified time as it is not possible from the Safari to obtain the modified time on upload.
3 Uploading files from the desktop
Files that are uploaded from a Mac, Windows or Linux Drive client, or via sync should have the timestamps fully preserved, but converted to UTC (with local time also being shown in browser and on desktop).
4 Uploading files over protocol adaptors
If files are uploaded over CloudDav or CloudFTP protocol adaptor then timestamp preservation depends on the client tool used and whether it issues the command to change the file timestamp.